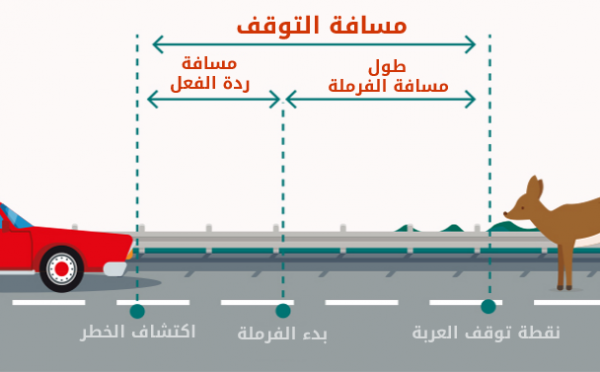
What is the reaction distance?
The reaction distance is the distance the car travels from the moment you discover the danger until you begin to react and brake
The reaction distance is affected by the speed of the vehicle and becomes longer, as the car covers a greater distance the higher the speed
For example
Twice faster speed = twice longer reaction distance.
Three times faster speed = three times longer reaction distance.
Five times faster speed = five times longer reaction distance .
We are talking about the length of the reaction distance, not the reaction time, so that you do not get confused
What is it and what does stopping distance mean?
It is the entire distance from the moment you discover the danger until the car stops completely
Reaction time is affected by the driver’s condition
It is negatively affected when the driver must choose between several actions, and the reaction time is also affected by the driver’s condition
If he drinks alcohol, takes drugs, or is tired, distracted, and other negative things.
The reaction time is shorter for experienced drivers, as the driver is always prepared to act and takes into account the risks that may occur.
You must also know that the reaction time does not change with increasing speed. “Time does not change “
The reaction time of a normal driver is approximately one second.
How much does the car travel per second?
When you drive at different speeds, the car travels different distances as well
To calculate how much your car travels per second, follow the following method
Remove the zero from the speed and multiply the number by the constant 3 and you will get the result per second
Some calculations of the distance a car travels per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 50 km per hour
Calculation: 5 times 3 equals approximately 15 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 60 km per hour
Calculation: 6 times 3 equals approximately 18 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 70 km per hour
Calculation: 7 times 3 equals approximately 21 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 80 km per hour
Calculation: 8 times 3 equals approximately 24 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 90 km per hour
Calculation: 9 times 3 equals approximately 27 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 100 km per hour
Calculation: 10 times 3 equals approximately 30 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 110 km per hour
Calculation: 11 times 3 equals approximately 33 meters per second
The distance the car travels at a speed of 120 km per hour
Calculation: 12 times 3 equals approximately 36 meters per second
The resulting distance is the driver’s reaction distance under normal conditions
Assuming that the driver acted and braked correctly within one second
When you are asked how much your car travels in a second, the above calculation method is used.
If the question is: How many times do you travel in a certain number of seconds? Multiply the result of the above calculation by the number of seconds.
Calculate braking distance
Calculating the braking distance is simple and easy, and you just have to follow the following method
To calculate the braking distance, we remove the zero from the speed and multiply the number by itself
Then we multiply the result by the constant number 0.4 and get the approximate braking distance.
Some braking distance calculations
Braking distance at speed 50 km per hour
Calculation: 5 times 5 equals 25 times 0.4 equals approximately 10 meters
The braking distance is 60 km per hour
Calculation: 6 times 6 equals 36 times 0.4 equals approximately 14.4 meters
The braking distance is 70 km per hour
Calculation: 7 times 7 equals 49 times 0.4 equals approximately 19.6 meters
The braking distance is 80 km per hour
Calculation: 8 times 8 equals 64 times 0.4 equals approximately 25.6 meters
The braking distance is 90 km per hour
Calculation: 9 times 9 equals 81 times 0.4 equals approximately 32.4 meters
The braking distance is at a speed of 100 km per hour
Calculation: 10 times 10 equals 100 times 0.4 equals approximately 40 meters
The braking distance at speed is 110 km per hour
Calculation: 11 times 11 equals 121 times 0.4 equals approximately 48.4 meters.
The braking distance is 120 km per hour
Calculation: 12 times 12 equals 144 times 0.4 equals approximately 57.6 meters.
We come to calculate the stopping distance, and here we must collect the reaction distance + the braking distance
Complete stopping distance when braking
When you want to correctly calculate the complete stopping distance when braking, assuming that the road is dry
If you have good tires and a fast and correct reaction, you must follow the following calculation method
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 50 km per hour
Reaction distance 15 meters + braking distance 10 meters equals approximately 25 meters stopping distance.
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 60 km per hour
Reaction distance 18 meters + braking distance 14.4 meters equals approximately 32.4 meters stopping distance
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 70 km per hour
Reaction distance 21 meters + braking distance 19.6 meters equals approximately 40.6 meters stopping distance
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 80 km per hour
Reaction distance 24 meters + braking distance 25.6 meters equals approximately 49.6 meters stopping distance
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 90 km per hour
Reaction distance 27 meters + braking distance 32.4 meters equals approximately 59.4 meters stopping distance
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 100 km per hour
Reaction distance 30 meters + braking distance 40 meters equals approximately 78.4 meters stopping distance
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 110 km per hour
Reaction distance 33 meters + braking distance 48.4 meters equals approximately 81.4 meters stopping distance
Complete stopping distance when braking at a speed of 120 km per hour
Reaction distance 36 meters + braking distance 57.6 meters equals approximately 93.6 meters stopping distance
Model for reaction distance, braking and stopping
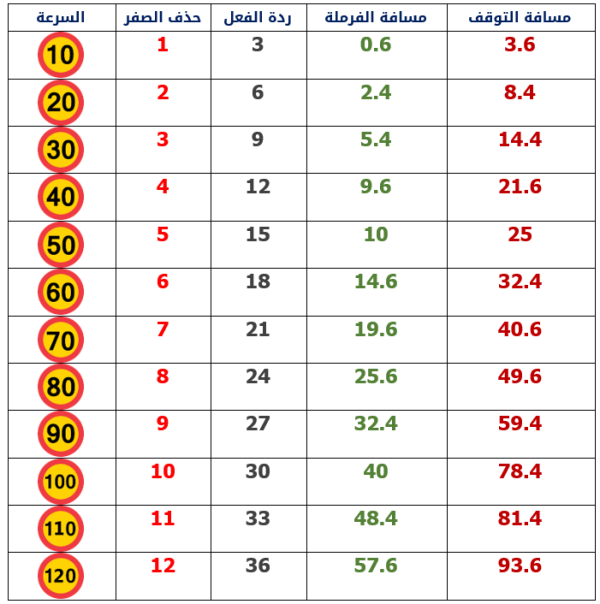
All the numbers and calculations mentioned are approximate numbers for the calculations, as there is no fixed base for the calculations, and there are several numbers that are relied upon to perform the calculation. The numbers may increase or decrease with a slight difference depending on the numbers used by each study source.
Time gain when driving
I will compare two different speeds so that you can get the information in a simple way. Suppose there is a driver driving at 70 km per hour and there is another driver driving at 90 km per hour. How much time does each driver need to cover one mile while driving?
We simply divide the hour, which is 60 minutes, by the speed without zero
- First driver Driving at a speed of 70 km per hour, we divide 60 minutes by the speed
Without the zero, it means 60 minutes divided by 7 equals 8.5 minutes. A driver driving at a speed of 70 km per hour needs to cover one mile. - Second driver Driving at a speed of 90 km per hour, we divide 60 minutes by the speed without zero, which means 60 minutes divided by 9 equals 6.6 minutes. A driver who drives at a speed of 90 km per hour needs to travel one mile.
Here we notice the time difference or time gain between the driver driving at a speed of 70 km
per hour, and the driver who drives at a speed of 90 km per hour is approximately two minutes in favor of the second driver
Another calculation for the time gain between two different speeds and let us notice the difference together
- First driver Driving at a speed of 40 km per hour
- Second driver Driving at a speed of 60 km per hour
Account for the first driver: We divide the hour, meaning 60 minutes, by the speed without zero
This means 60 divided by 4 equals the 15 minutes it takes the first driver to cover one mile.
Account for the second driver: We divide the hour, meaning 60 minutes, by the speed without zero
This means 60 divided by 6 equals 10 minutes it takes the second driver to cover one mile.
Here the difference between the two speeds is 5 minutes in favor of the second driver, who is driving at a speed of 60 km, meaning that he needs 10 minutes at his current speed of 60 km per hour to cover one mile, in contrast to the first driver, who is driving at a speed of 40 km, who needs 15 minutes to cover one mile.
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
- Access to all lessons
- Accessing 1400 questions
- Accessing traffic signs
- Computer or Mobile Login
- Study without ads
- View test results
- Instant activation
